Neuroscience-Driven Innovation
The Science Behind
Rafias
Rafias’ research builds on over a decade of neuroscience and epigenetics work at the University of Pennsylvania’s Heller Lab. Our approach focuses on activating the transcription factor, Nr4a1, to counter the neuroadaptations that drive addiction and promote recovery pathways.
The Science
Addiction is a chronic, relapsing disorder marked by persistent neuroadaptations that continue long after drug use stops. During abstinence, relapse risk increases due to dopamine-regulated reward circuits, impaired homeostasis, and heightened cue sensitivity. Rafias focuses on restoring these disrupted systems.
This approach builds on published work from the Heller Lab, including studies demonstrating Nr4a1’s role in regulating neural adaptations that contribute to addiction and relapse.

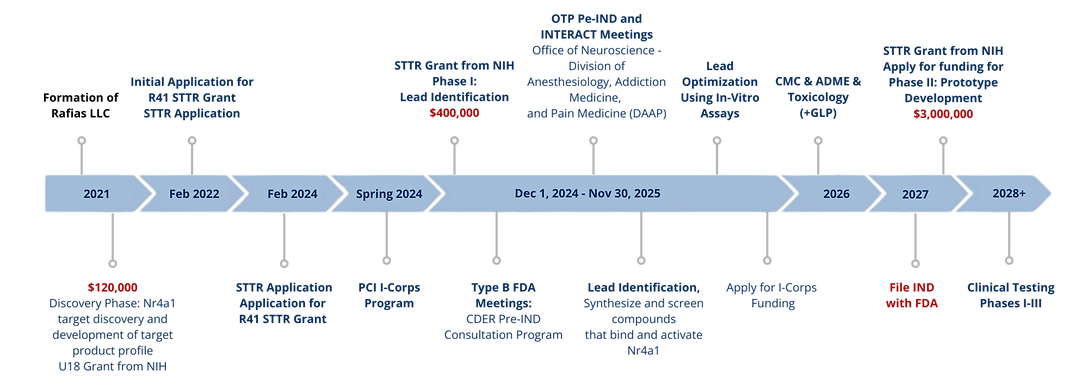
Scientific Development Path

2021
2023
2025
2028
NIH U18 Grant — Target Discovery
2025
2027
2028
Supports mechanistic validation of Nr4a1 as a therapeutic target in addiction, establishing its role in neural homeostasis and relapse biology.
NIH STTR Phase I — Lead Identification
2025
2027
2028
Funds the design and early evaluation of Nr4a1-directed molecules, identifying promising candidates for further optimization.
NIH STTR Phase II — Prototype Development (pending)
2025
2027
2028
Supports optimization and preclinical testing of therapeutic prototypes aimed at restoring recovery pathways during abstinence.
Preclinical Milestones — IND-Enabling Work (in progress)
2025
2027
2028
Advancing pharmacology, safety, and proof-of-concept studies required to prepare for IND submission.
IND Submission (planned)
2025
2027
2028
Regulatory milestone preceding human trials.
Clinical Trials — Phases I–III (future milestone)
2025
2027
2028
Evaluation of safety, dosing, efficacy, and long-term relapse-prevention outcomes.
Funding & Regulatory Milestones
This timeline outlines Rafias’ non-dilutive funding progress and regulatory milestones from early discovery through IND submission. It highlights secured NIH support, pending grant applications, and the planned preclinical and clinical steps required to advance our Nr4a1-targeting therapeutics.